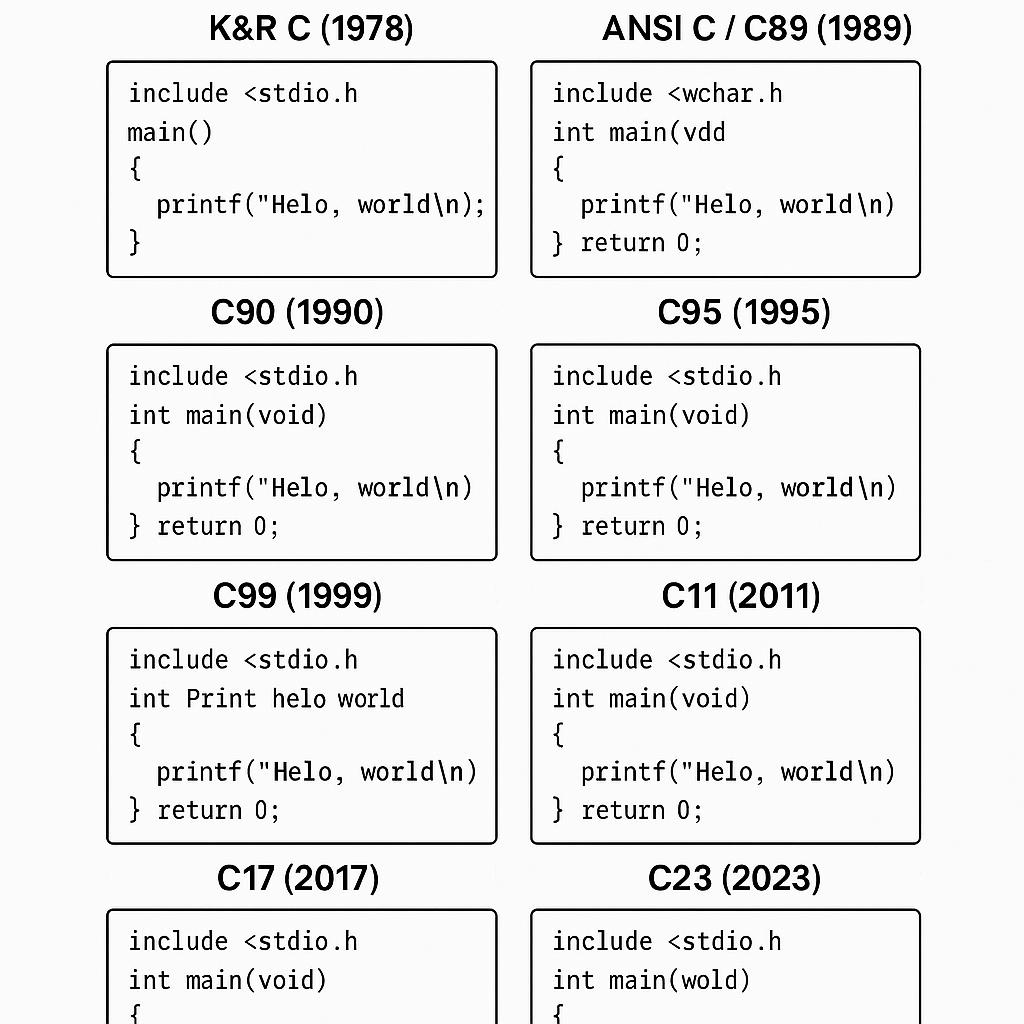
📌 C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis with Hello World
The evolution of C can be understood best through small, simple examples. The Hello World program has always been the first stepping stone for new learners, and by tracking how it changes across different standards, we gain a clear timeline of how C itself has matured. In this expanded article, C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis, we don’t just show the syntax but also explain the motivation and reasoning behind the changes.
Table of Contents
K&R C (1978) – The Origin
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
printf("Hello, world\n");
}
- What it shows: Early C did not require
mainto declare a return type. - Why it mattered: At the time, portability was not a big concern; most C programs were written for UNIX systems where defaults were assumed.
- Analysis: In C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis, this version marks the starting point of structured programming in C. It feels minimal but also error-prone because the compiler had no strict type checking.
ANSI C / C89 (1989) – Standardization Arrives
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
printf("Hello, world\n");
return 0;
}
- What it shows: Function prototypes and explicit return types became mandatory.
- Why it mattered: Software was expanding to different systems, and consistency was essential.
- Analysis: In C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis, C89 represents the first serious attempt to make C portable across compilers and operating systems.
C90 (1990) – International Acceptance
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
printf("Hello, world\n");
return 0;
}
- What it shows: No syntactic difference from C89.
- Why it mattered: ISO ratified ANSI C, which meant C became a true global standard.
- Analysis: From the perspective of C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis, C90 is less about new syntax and more about global agreement.
C95 (1995) – Unicode Support
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void) {
wprintf(L"Hello, world\n");
return 0;
}
- What it shows: Wide characters allow multilingual text.
- Why it mattered: The world was moving beyond ASCII; software needed to handle global languages.
- Analysis: In C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis, C95 illustrates how the language adapted to globalization and internationalization.
C99 (1999) – Modern Features
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
// Print hello world in C99
printf("Hello, world\n");
return 0;
}
- What it shows: C99 introduces single-line comments (
//) and other modern tools. - Why it mattered: Developers wanted cleaner syntax and new data types (
long long,_Bool). - Analysis: Within C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis, C99 is seen as the most revolutionary update, bringing C closer to the flexibility of C++.
C11 (2011) – Concurrency and Safety
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
printf("Hello, world\n");
return 0;
}
- What it shows: Hello World remains unchanged.
- Why it mattered: Under the hood, C11 added threads (
<threads.h>), atomics, and static assertions for safer, concurrent programs. - Analysis: In C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis, C11 demonstrates how C kept up with multi-core processors and modern computing needs.
C17 (2017) – Stability Release
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
printf("Hello, world\n");
return 0;
}
- What it shows: No visible changes.
- Why it mattered: Focused on clarifying the C11 specification and removing ambiguities.
- Analysis: From C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis, C17 is not innovative but ensures the language remains consistent across compilers.
C23 (2023) – The Latest Evolution
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
printf("Hello, world\n");
return 0;
}
- What it shows: Hello World is unchanged, but the language adds modern concepts.
- Why it mattered: Introduces
nullptr,typeof, and#embedto make C more convenient in modern contexts. - Analysis: In C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis, C23 proves that even after decades, C is still evolving while retaining its minimalist Hello World structure.
✅ Final Thoughts
The Hello World program demonstrates that while C’s syntax has stayed simple, the context around it—portability, globalization, concurrency, and modern programming practices—has transformed dramatically. C Language Standards: A Comparative Analysis shows that C continues to balance tradition with innovation. By looking at these small examples, learners and developers can see how a simple “Hello, world” reflects the philosophy and evolution of the entire C language.
Awesome—here’s a clean, English implementation of the console vending machine with English comments, plus standards-specific versions so you can compile under strict C89 and modern C11/C17/C23. I also note what changes C99 enables.
Let’s make a vending machine
# Strict ANSI C89
gcc -std=c89 -Wall -Wextra -O2 vending_c89.c -o vending89
# C99 (or newer)
gcc -std=c99 -Wall -Wextra -O2 vending_c11.c -o vending99
# C11 / C17 / C23 (same source works)
gcc -std=c11 -Wall -Wextra -O2 vending_c11.c -o vending11
gcc -std=c17 -Wall -Wextra -O2 vending_c11.c -o vending17
gcc -std=c23 -Wall -Wextra -O2 vending_c11.c -o vending23
✅ Version 1 — C11/C17/C23 (modern baseline)
File:
vending_c11.c
Uses<stdbool.h>,long long,//comments, and a_Static_assertthat’s valid since C11.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// ---- Configuration ---------------------------------------------------------
#define MAX_PRODUCTS 6
#define ADMIN_PIN "1234"
// Denominations in KRW (assume the machine can return exact change in these)
static const int DENOMS[] = {1000, 500, 100, 50, 10};
static const int NDENOMS = (int)(sizeof(DENOMS) / sizeof(DENOMS[0]));
// Ensure all denominations are multiples of 10 (compile-time check, C11+)
_Static_assert(1000 % 10 == 0 && 500 % 10 == 0 && 100 % 10 == 0 &&
50 % 10 == 0 && 10 % 10 == 0,
"All denominations must be multiples of 10");
// ---- Data Types ------------------------------------------------------------
typedef struct {
char name[32]; // Product display name
int price; // Price in KRW (multiple of 10)
int stock; // Units remaining
} Product;
typedef enum {
STATE_IDLE = 0,
STATE_COLLECTING,
STATE_DISPENSE,
STATE_CHANGE
} VMState;
// ---- Globals (small demo) --------------------------------------------------
static Product products[MAX_PRODUCTS] = {
{"Water", 800, 10},
{"Cola", 1400, 8},
{"OrangeJuice",1200, 7},
{"Coffee", 900, 12},
{"Tea", 700, 15},
{"Snack", 1100, 9}
};
static int balance = 0; // Money inserted by the current user
static long long sales = 0; // Cumulative sales (KRW)
// ---- Utilities -------------------------------------------------------------
static void line(void) { puts("--------------------------------------------------"); }
static void print_products(void) {
line();
puts("Products:");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_PRODUCTS; ++i) {
printf(" [%d] %-12s Price: %4d Stock: %d\n",
i, products[i].name, products[i].price, products[i].stock);
}
line();
}
static void print_menu(void) {
puts("[Menu]");
puts(" 1) Insert Money");
puts(" 2) Select Product");
puts(" 3) Cancel (Refund)");
puts(" 4) Admin Mode");
puts(" 0) Exit");
line();
printf("Current Balance: %d KRW\n", balance);
}
static bool is_valid_denom(int v) {
for (int i = 0; i < NDENOMS; ++i) if (DENOMS[i] == v) return true;
return false;
}
static void flush_stdin(void) {
int c;
while ((c = getchar()) != '\n' && c != EOF) { /* discard */ }
}
// ---- Core actions ----------------------------------------------------------
static void insert_money(void) {
int v;
printf("Insert (10,50,100,500,1000): ");
if (scanf("%d", &v) != 1) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid input."); return; }
if (!is_valid_denom(v)) { puts("Unsupported denomination."); return; }
balance += v;
printf("Inserted %d. Balance: %d\n", v, balance);
}
static void give_change(int amount) {
if (amount <= 0) { puts("No change."); return; }
puts("Change:");
for (int i = 0; i < NDENOMS; ++i) {
int cnt = amount / DENOMS[i];
if (cnt > 0) {
printf(" %4d x %d\n", DENOMS[i], cnt);
amount %= DENOMS[i];
}
}
if (amount != 0) {
// Theoretically unreachable if all prices and input are multiples of 10
printf(" ** Unreturnable remainder: %d **\n", amount);
}
}
static void select_product(void) {
int idx;
print_products();
printf("Select product index: ");
if (scanf("%d", &idx) != 1) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid input."); return; }
if (idx < 0 || idx >= MAX_PRODUCTS) { puts("Out of range."); return; }
Product *p = &products[idx];
if (p->stock <= 0) { puts("Out of stock."); return; }
if (balance < p->price) {
printf("Insufficient balance. Need %d more.\n", p->price - balance);
return;
}
// Dispense and account
p->stock -= 1;
balance -= p->price;
sales += p->price;
printf("Dispensing: %s\n", p->name);
if (balance > 0) {
give_change(balance);
balance = 0;
} else {
puts("No change.");
}
}
static void cancel_refund(void) {
if (balance == 0) { puts("Nothing to refund."); return; }
printf("Refunding %d...\n", balance);
give_change(balance);
balance = 0;
}
// ---- Admin features --------------------------------------------------------
static void admin_inventory(void) {
int idx, qty;
print_products();
printf("Restock product index: ");
if (scanf("%d", &idx) != 1) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid input."); return; }
if (idx < 0 || idx >= MAX_PRODUCTS) { puts("Out of range."); return; }
printf("Add quantity: ");
if (scanf("%d", &qty) != 1 || qty < 0) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid qty."); return; }
products[idx].stock += qty;
printf("Restocked. %s stock: %d\n", products[idx].name, products[idx].stock);
}
static void admin_change_price(void) {
int idx, price;
print_products();
printf("Change price index: ");
if (scanf("%d", &idx) != 1) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid input."); return; }
if (idx < 0 || idx >= MAX_PRODUCTS) { puts("Out of range."); return; }
printf("New price (>=10, multiple of 10): ");
if (scanf("%d", &price) != 1 || price < 10 || price % 10 != 0) {
flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid price."); return;
}
products[idx].price = price;
printf("Updated. %s price: %d\n", products[idx].name, products[idx].price);
}
static void admin_mode(void) {
char pin[32];
printf("Enter admin PIN: ");
scanf("%31s", pin);
if (strcmp(pin, ADMIN_PIN) != 0) { puts("Wrong PIN."); return; }
int sel = -1;
do {
line();
puts("[Admin]");
puts(" 1) Restock");
puts(" 2) Change Price");
puts(" 3) View Sales");
puts(" 0) Back");
line();
printf("Select: ");
if (scanf("%d", &sel) != 1) { flush_stdin(); sel = -1; }
switch (sel) {
case 1: admin_inventory(); break;
case 2: admin_change_price(); break;
case 3: printf("Total Sales: %lld KRW\n", sales); break;
case 0: puts("Exit admin."); break;
default: puts("Invalid.");
}
} while (sel != 0);
}
// ---- Main loop -------------------------------------------------------------
int main(void) {
VMState state = STATE_IDLE;
int sel;
puts("=== Vending Machine (C11/C17/C23) ===");
while (1) {
switch (state) {
case STATE_IDLE:
case STATE_COLLECTING:
print_products();
print_menu();
printf("Select: ");
if (scanf("%d", &sel) != 1) { flush_stdin(); sel = -1; }
if (sel == 0) { puts("Bye!"); return 0; }
else if (sel == 1) { insert_money(); state = STATE_COLLECTING; }
else if (sel == 2) { select_product(); state = STATE_IDLE; }
else if (sel == 3) { cancel_refund(); state = STATE_IDLE; }
else if (sel == 4) { admin_mode(); state = STATE_IDLE; }
else { puts("Invalid menu."); }
break;
case STATE_DISPENSE:
case STATE_CHANGE:
// Not used in this demo; handled inside select/refund paths.
state = STATE_IDLE;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
✅ Version 2 — Strict ANSI C89
File:
vending_c89.c
Key differences to satisfy C89:
- No
<stdbool.h>→ define our ownBOOL.- No
//comments → use/* ... */only.- All variable declarations at the start of a block.
- Avoid
long long→ uselongforsales.- No mixed declarations/statements in
forloops.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* ---- Basic boolean replacement for C89 ---- */
typedef int BOOL;
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
/* ---- Configuration ---- */
#define MAX_PRODUCTS 6
#define ADMIN_PIN "1234"
/* Denominations (KRW) */
static const int DENOMS[] = {1000, 500, 100, 50, 10};
static const int NDENOMS = (int)(sizeof(DENOMS) / sizeof(DENOMS[0]));
/* ---- Data Types ---- */
typedef struct {
char name[32];
int price;
int stock;
} Product;
typedef enum {
STATE_IDLE = 0,
STATE_COLLECTING,
STATE_DISPENSE,
STATE_CHANGE
} VMState;
/* ---- Globals ---- */
static Product products[MAX_PRODUCTS] = {
{"Water", 800, 10},
{"Cola", 1400, 8},
{"OrangeJuice", 1200, 7},
{"Coffee", 900, 12},
{"Tea", 700, 15},
{"Snack", 1100, 9}
};
static int balance = 0;
static long sales = 0; /* Use long, since long long is not standard in C89 */
/* ---- Utilities ---- */
static void line(void) { puts("--------------------------------------------------"); }
static void flush_stdin(void) {
int c;
while ((c = getchar()) != '\n' && c != EOF) { /* discard */ }
}
static void print_products(void) {
int i;
line();
puts("Products:");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_PRODUCTS; ++i) {
printf(" [%d] %-12s Price: %4d Stock: %d\n",
i, products[i].name, products[i].price, products[i].stock);
}
line();
}
static void print_menu(void) {
puts("[Menu]");
puts(" 1) Insert Money");
puts(" 2) Select Product");
puts(" 3) Cancel (Refund)");
puts(" 4) Admin Mode");
puts(" 0) Exit");
line();
printf("Current Balance: %d KRW\n", balance);
}
static BOOL is_valid_denom(int v) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < NDENOMS; ++i) {
if (DENOMS[i] == v) return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
/* ---- Core actions ---- */
static void insert_money(void) {
int v;
printf("Insert (10,50,100,500,1000): ");
if (scanf("%d", &v) != 1) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid input."); return; }
if (!is_valid_denom(v)) { puts("Unsupported denomination."); return; }
balance += v;
printf("Inserted %d. Balance: %d\n", v, balance);
}
static void give_change(int amount) {
int i, cnt;
if (amount <= 0) { puts("No change."); return; }
puts("Change:");
for (i = 0; i < NDENOMS; ++i) {
cnt = amount / DENOMS[i];
if (cnt > 0) {
printf(" %4d x %d\n", DENOMS[i], cnt);
amount %= DENOMS[i];
}
}
if (amount != 0) {
printf(" ** Unreturnable remainder: %d **\n", amount);
}
}
static void select_product(void) {
int idx;
Product *p;
print_products();
printf("Select product index: ");
if (scanf("%d", &idx) != 1) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid input."); return; }
if (idx < 0 || idx >= MAX_PRODUCTS) { puts("Out of range."); return; }
p = &products[idx];
if (p->stock <= 0) { puts("Out of stock."); return; }
if (balance < p->price) {
printf("Insufficient balance. Need %d more.\n", p->price - balance);
return;
}
/* Dispense and account */
p->stock -= 1;
balance -= p->price;
sales += p->price;
printf("Dispensing: %s\n", p->name);
if (balance > 0) {
give_change(balance);
balance = 0;
} else {
puts("No change.");
}
}
static void cancel_refund(void) {
if (balance == 0) { puts("Nothing to refund."); return; }
printf("Refunding %d...\n", balance);
give_change(balance);
balance = 0;
}
/* ---- Admin ---- */
static void admin_inventory(void) {
int idx, qty;
print_products();
printf("Restock product index: ");
if (scanf("%d", &idx) != 1) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid input."); return; }
if (idx < 0 || idx >= MAX_PRODUCTS) { puts("Out of range."); return; }
printf("Add quantity: ");
if (scanf("%d", &qty) != 1 || qty < 0) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid qty."); return; }
products[idx].stock += qty;
printf("Restocked. %s stock: %d\n", products[idx].name, products[idx].stock);
}
static void admin_change_price(void) {
int idx, price;
print_products();
printf("Change price index: ");
if (scanf("%d", &idx) != 1) { flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid input."); return; }
if (idx < 0 || idx >= MAX_PRODUCTS) { puts("Out of range."); return; }
printf("New price (>=10, multiple of 10): ");
if (scanf("%d", &price) != 1 || price < 10 || price % 10 != 0) {
flush_stdin(); puts("Invalid price."); return;
}
products[idx].price = price;
printf("Updated. %s price: %d\n", products[idx].name, products[idx].price);
}
static void admin_mode(void) {
char pin[32];
int sel;
printf("Enter admin PIN: ");
scanf("%31s", pin);
if (strcmp(pin, ADMIN_PIN) != 0) { puts("Wrong PIN."); return; }
sel = -1;
do {
line();
puts("[Admin]");
puts(" 1) Restock");
puts(" 2) Change Price");
puts(" 3) View Sales");
puts(" 0) Back");
line();
printf("Select: ");
if (scanf("%d", &sel) != 1) { flush_stdin(); sel = -1; }
switch (sel) {
case 1: admin_inventory(); break;
case 2: admin_change_price(); break;
case 3: printf("Total Sales: %ld KRW\n", sales); break;
case 0: puts("Exit admin."); break;
default: puts("Invalid.");
}
} while (sel != 0);
}
/* ---- Main ---- */
int main(void) {
VMState state = STATE_IDLE;
int sel;
puts("=== Vending Machine (ANSI C89) ===");
for (;;) {
switch (state) {
case STATE_IDLE:
case STATE_COLLECTING:
print_products();
print_menu();
printf("Select: ");
if (scanf("%d", &sel) != 1) { flush_stdin(); sel = -1; }
if (sel == 0) { puts("Bye!"); return 0; }
else if (sel == 1) { insert_money(); state = STATE_COLLECTING; }
else if (sel == 2) { select_product(); state = STATE_IDLE; }
else if (sel == 3) { cancel_refund(); state = STATE_IDLE; }
else if (sel == 4) { admin_mode(); state = STATE_IDLE; }
else { puts("Invalid menu."); }
break;
case STATE_DISPENSE:
case STATE_CHANGE:
state = STATE_IDLE;
break;
}
}
/* Unreachable */
/* return 0; */
}
ℹ️ What changes in C99?
If you compile vending_c11.c with -std=c99, it already conforms. C99 mainly lets you:
- Use
//comments (already in the C11 version). - Declare loop variables inside
for (int i = 0; ...). - Use
long long(also used in the C11 version). - No
_Static_assert(that’s C11), but you can emulate with a macro if needed.
So for C99, use the C11 file but remove the _Static_assert line (or keep it—most compilers accept it as an extension, but strict C99 does not).
✅ Helpful External Links (English)
- ISO/IEC 9899:2018 (C17 Standard) – Overview
https://www.iso.org/standard/74528.html
→ Official ISO page for the C17 standard, with details about the scope and purpose. - GNU C Standards Documentation
https://gcc.gnu.org/c99status.html
→ GCC’s documentation showing the level of support for different C standards (C89, C99, C11, etc.). - cppreference – C Standard Overview
https://en.cppreference.com/w/c/
→ A comprehensive, easy-to-read reference covering C standards, syntax, and standard library functions. - ANSI C (C89) Rationale
https://port70.net/~nsz/c/c89/c89-draft.html
→ Draft rationale document explaining why ANSI C introduced certain changes. - Clang/LLVM C Standard Support
https://clang.llvm.org/cstatus.html
→ Explains how Clang implements different C standard versions. - Modern C Programming (C11/C17/C23)
https://modernc.gforge.inria.fr/
→ Educational site focusing on writing portable and modern C code with examples.